
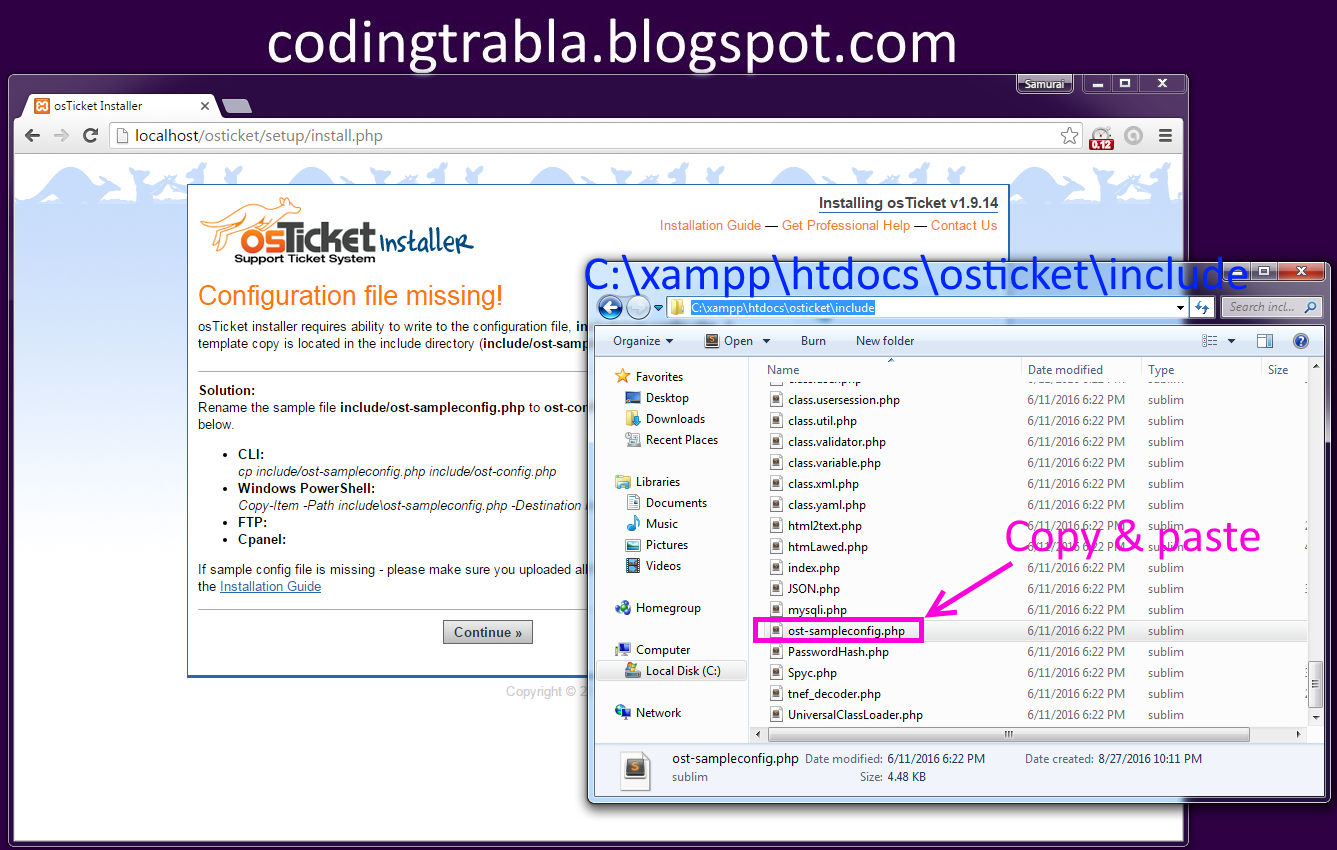
none, off never make backups (even if –backup is given).The version control method may be selected via the –backup option or through the VERSION_CONTROL environment variable. The backup suffix is ‘~’, unless set with –suffix or SIMPLE_BACKUP_SUFFIX. Use –reflink=never to ensure a standard copy is performed. If this is not possible the copy fails, or if –reflink=auto is specified, fall back to a standard copy. When –reflink is specified, perform a lightweight copy, where the data blocks are copied only when modified. Use –sparse=never to inhibit creation of sparse files. Specify –sparse=always to create a sparse DEST file whenever the SOURCE file contains a long enough sequence of zero bytes. That is the behavior selected by –sparse=auto. Mandatory arguments to long options are mandatory for short options too.īy default, sparse SOURCE files are detected by a crude heuristic and the corresponding DEST file is made sparse as well. cp -helpĬopy SOURCE to DEST, or multiple SOURCE(s) to DIRECTORY. “cp” command related information can be obtained with “–help”. Done, now you’ve already copied the files.Use the “cp” with the “-i” option to confirm before copying it.This will copy all files to directory called “Documents”. Copy all files to another directory, Use wildcard (*).This will copy “doc.txt”, “image.jpg”, and “docs.pdf” to directory called “Documents”. Copy multiple files in the current working directory to another directory.Ĭp doc.txt image.jpg docs.pdf /home/username/Documents.This will copy “doc.txt” to directory called “Documents”. Copy a file in the current directory to another directory.The syntax for using the “cp” command as shown below.Ĭp.Use “cp” command with option as alternative and specify the “file-name.ext”.Keep on the current working directory or go to the specific directory (use “cd” to change directory) that you want to copy the file inside it.This is one of the most common administrative tasks you can perform when working on terminal with the linux command line. “cp” command is used to copy files or group of files or directory from the current directory to a different directory. You can easily copy file in linux via terminal on your system using the command line with the following methods cp, and Information.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
